Is your computer vulnerable to attack from WannaCry ransomware? Read on as we explore all there is to know about the WannaCry ransomware attack.
In this article, you will learn:
- What WannaCry ransomware is
- How the WannaCry ransomware attack worked
- The impact of the WannaCry ransomware attack
- How to protect your computer from ransomware.
WannaCry ransomware explained
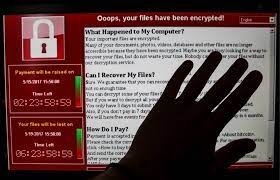
WannaCry is an example of crypto-ransomware, a malicious software (malware) cybercriminals use to extort money from individuals, corporations, hospitals, utilities, and governments—basically, anyone who has value and is on the internet.
Ransomware does this by either encrypting valuable files so you cannot read them or by locking you out of your computer, so you cannot use it.
Ransomware that uses encryption is called crypto-ransomware. The type that locks you out of your computer is called locker ransomware.
Like other types of crypto-ransomware, WannaCry takes your data hostage, promising to return it if you pay a ransom.
WannaCry targets computers using Microsoft Windows as an operating system. It encrypts data and demands a ransom payment in cryptocurrency. Typically, Bitcoin is asked to restore the data.
What was the WannaCry ransomware attack?
The WannaCry ransomware attack was a global epidemic that took place in May 2017.
This ransomware attack spread through computers operating Microsoft Windows. The user’s files were held hostage, and a Bitcoin ransom was demanded their return.
Were it not for the continued use of outdated computer systems and poor education about the need to update software, the damage caused by this attack could have been avoided.

How does a WannaCry attack work?
The cybercriminals responsible for the attack took advantage of a weakness in the Microsoft Windows operating system using a hack that was allegedly developed by the United States National Security Agency.
Known as EternalBlue, this hack was made public by a group of hackers called the Shadow Brokers before the WannaCry attack.
Microsoft released a security patch that protected users’ systems against this exploit almost two months before the WannaCry ransomware attack began. Unfortunately, many individuals and organizations do not regularly update their operating systems and are exposed to attacks.
Those that had not run a Microsoft Windows update before the attack did not benefit from the patch, and the vulnerability exploited by EternalBlue left them open to attack.
When it first happened, people assumed that the WannaCry ransomware attack had initially spread through a phishing campaign (a phishing campaign is where spam emails with infected links or attachments lure users to download malware). However, EternalBlue was the exploit that allowed WannaCry to propagate and spread, with DoublePulsar being the ‘backdoor’ installed on the compromised computers (used to execute WannaCry).
What would happen if the WannaCry ransom was not paid?
The attackers demanded $300 worth of bitcoins and then later increased the ransom demand to $600 worth of bitcoins. If victims did not pay the ransom within three days, the WannaCry ransomware attack victims were told that their files would be permanently deleted.
The advice regarding ransom payments is not to cave into the pressure. Always avoid paying a ransom, as there is no guarantee that your data will be returned, and every payment validates the criminals’ business model, making future attacks more likely.
This advice proved wise during the WannaCry attack, as the coding used was reportedly faulty. When victims paid their ransom, the attackers could not associate the payment with a specific victim’s computer.
There’s some doubt about whether anyone got their files back. Some researchers claimed that no one got their data back. However, a company called F-Secure claimed that some did. This is a stark reminder of why paying the ransom is never a good idea if you experience a ransomware attack.
What impact did the WannaCry attack have?
The WannaCry ransomware attack hit around 230,000 computers globally.
One of the first companies affected was the Spanish mobile company, Telefónica. By May 12th, thousands of NHS hospitals and surgeries across the UK were affected.
A third of NHS hospital trusts were affected by the attack. Terrifyingly, ambulances were reportedly rerouted, leaving people needing urgent care in need. It was estimated to cost the NHS a whopping £92 million after 19,000 appointments were canceled due to the attack.
As the ransomware spread beyond Europe, computer systems in 150 countries were crippled. The WannaCry ransomware attack had a substantial financial impact worldwide. It is estimated that this cybercrime caused $4 billion in losses globally.
Ransomware protection
Now that you understand how the WannaCry ransomware attack took place and its impact, let’s consider how to protect yourself from ransomware.
Here are our top tips:
Update your software and operating system regularly
Computer users became victims of the WannaCry attack because they had not updated their Microsoft Windows operating system.
Had they updated their operating systems regularly, they would have benefited from the security patch that Microsoft released before the attack.
This patch removed the vulnerability that EternalBlue exploited to infect computers with WannaCry ransomware.
Be sure to keep your software and operating system updated. This is an essential ransomware protection step.
Do not click on suspicious links
If you open an unfamiliar email or visit a website you do not trust, do not click on any links. Clicking on unverified links could trigger a ransomware download.
Never open untrusted email attachments
Avoid opening any email attachments unless you are sure they are safe. Do you know and trust the sender? Is it clear what the attachment extension is it? Were you expecting to receive the attached file?
If the attachment asked you to enable macros to view it, stay well clear. Do not enable macros or open the attachment, as this is a common way ransomware and other types of malware are spread.
Do not download from untrusted websites
Downloading files from unknown sites increases the risk of downloading ransomware. Only download files from websites you trust.
Avoid unknown USBs
Do not insert USBs or other removal storage devices into your computer if you do not know where they came from. They could be infected with ransomware.