A wide area network (WAN) is any network that extends over a large geographic area, usually connecting multiple local area networks (LANs).
What is a wide area network (WAN)?
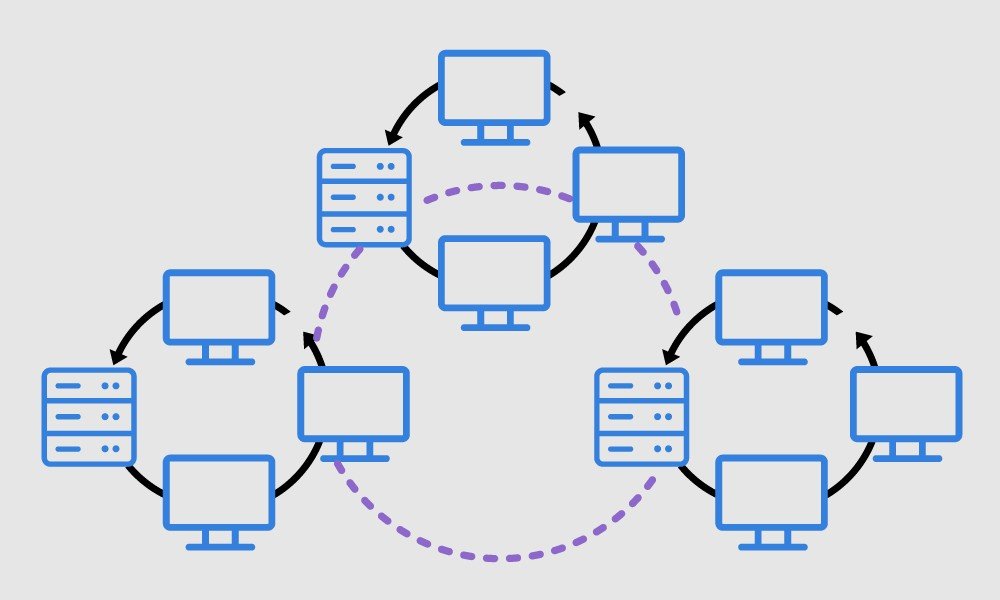
A vast area network (WAN) is an extensive computer network that connects groups of computers over large distances. Large businesses often use WANs to connect their office networks; each office typically has its own local area network (LAN), which is connected via a WAN. These long connections may be formed in several ways, including leased lines, VPNs, or IP tunnels (see below).
The definition of what constitutes a WAN is pretty broad. Technically, any extensive network spreading over a wide geographic area is a WAN. The Internet itself is considered a WAN.

What is a LAN?
A local area network (LAN) is confined to a small, localized area. Home WiFi networks and small business networks are typical examples of LANs. Typically, whoever manages the LAN also manages the networking equipment it uses. A small business, for instance, will manage the routers and switches involved in setting up the LAN.
WAN vs. LAN
LANs typically exist in a contained area and share a single central Internet connection point. WANs are designed to provide network connectivity over long distances and are usually made up of several connected LANs. An organization that sets up its own WAN will almost always rely on network infrastructure outside its control. For example, a company with an office in Paris and an office in New York will have to send data between these offices over undersea cables that cross the Atlantic Ocean.
Usually, a WAN includes multiple routers and switches. A LAN only needs one router to connect to the Internet or other LANs, although it may also use switches.
What is a leased line?
One way organizations connect their LANs to form a WAN is by using a leased line. A leased line is a direct network connection rented from a large network provider such as an ISP. Building their own physical network infrastructure—including cables, routers, and Internet exchange points across hundreds or thousands of miles—would be almost impossible for most organizations. So, instead, they lease a direct, dedicated connection from a company with this infrastructure.
What is tunneling? What is a VPN?
If a company does not want to pay for a leased line, they can connect their LANs using tunneling. In networking, tunneling is a method for encapsulating data packets* within other data packets so that they go somewhere they would not otherwise go. Imagine mailing an envelope inside another envelope, with both envelopes having a different address, so the internal envelope gets mailed from the external envelope’s destination address. That is the general idea of tunneling, except data is contained within packets instead of envelopes.
Some network tunnels are encrypted to protect the packets’ contents from anyone who might intercept them en route. Encrypted tunnels are called VPNs or virtual private networks. VPN connections between WANs are more secure than unencrypted tunneling connections. IPsec is one standard VPN encryption protocol.
The main drawback of using tunneling to connect LANs is that tunneling increases overhead; it takes more computing power and, thus, more time to send packets in this way. Encapsulating and encrypting each packet slows communications, just as stuffing an envelope twice instead of once slows down how quickly it can be placed in the mail. Additionally, encapsulated packets may end up more significant than some routers on the network can handle, resulting in fragmentation and adding more delays.
*All data sent over a network is broken up into packets, smaller chunks of data. Each packet includes information about the packet’s origin, destination, and position in the series of packets.
What is a software-defined WAN (SD-WAN)?
A software-defined WAN, or SD-WAN, is a more flexible WAN architecture that can take advantage of multiple hardware platforms and connectivity options. The controlling software works with any networking hardware.
SD-WANs are one form of software-defined networking (SDN), a category of technologies that make it possible to manage networks with software. They are also a key component of secure access service edge (SASE) solutions, which combine networking and network security functions into a single, cloud-based service.
What is WAN-as-a-service?
WAN-as-a-service is a cloud-based WAN model. It is designed to replace legacy WAN configurations that rely on hardware, use connectivity protocols like multiprotocol label switching (MPLS), and are difficult to scale up. As WAN-as-a-service is offered via the cloud, customers only need Internet connectivity and can configure their WAN using software instead of hardware appliances.